Amadeus has unveiled a 2.1 software version for its immersive platforms – Holophonix Servers, and the Holophonix Native app for macOS – at the 2023 Integrated Systems Europe (ISE) conference in Barcelona. This is in addition to the announcement of two new configurations for its hardware processor, offering 128 outputs and 64 outputs. The new 2.1 software update is free, available now.
The new Holophonix hardware configurations are available for order now and feature redesigned rear panels with Neutrik-housed connectors integrated into the aluminium chassis, including one powerCON mains connector, three etherCON connectors for remote control and Dante redundant protocol, as well as HDMI and USB 3.2 connectors for service. The updated Holophonix processor models are 1.6 times faster than the previous model. The Holophonix 128 model offers 128 x 128 I/O at 96kHz in Dante AoIP format, while the new Holophonix 64 model offers 128 inputs for 64 outputs at 96kHz in Dante AoIP format.
“Machined in three dimensions from a solid aluminium block – taking more than 20 hours to complete – the new Holophonix processor enclosure embodies all the technicality embedded and hidden within this unique tool,” said Gaetan Byk, Amadeus CEO. “We designed some interesting features for the Wave Field Synthesis (WFS) algorithm over the last months, which figure among the most interesting algorithms built-in Holophonix, used in 90% of the systems that we deploy.”
“Recent work conducted at IRCAM helped us extend and improve our WFS rendering engine,” said Thibaut Carpentier, researcher at IRCAM, lead developer, and head of the SPAT project. “Originally restricted to 2D dense linear arrays of loudspeakers, the WFS approach has been generalised and is now compatible with arbitrary 3D loudspeaker layouts. This features several optimisations for large arrays, or linear arrays with large spacing in-between loudspeakers, as well as 3D dome-like speaker layouts.”
“With immersive speaker systems, users can now create virtual sounds anywhere in 3D space; full-3D WFS gains and delays are computed in real-time, generating a convincing sound field that overcomes limitations of other techniques such as Ambisonics,” added Carpentier.
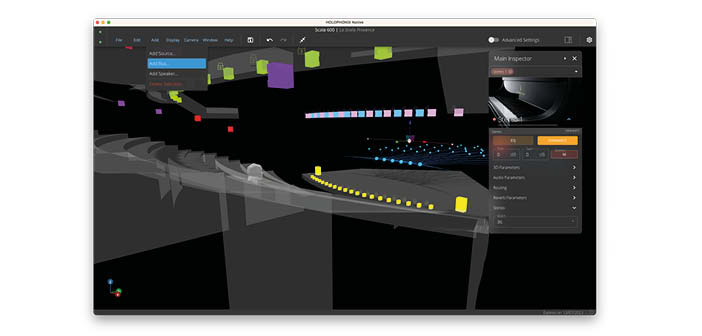
The new Holophonix 2.1 update features, among other improvements, a new 3D-native computation of gains and delays for the WFS algorithm, a new ‘Minimal Delay’ mode, and a new parameter called Large Stage Optimizer (LSO), designed to optimise intelligibility for spectators sitting in the very first rows.
“The Minimal Delay parameter option is only available for the WFS algorithm,” said Adrien Zanni, researcher and developer at Amadeus for the Holophonix project. “When disabled, the WFS bus calculates the source’s delays and gains related to their real position from the speaker array. Thus, moving a source away from the speaker array increases the overall delay and latency. When enabled, the bus calculates the source’s delays and gains but subtracts the distance to the nearest speaker, resulting in lower latency.”
“The LSO was originally designed for the Avignon Palace of Popes Cour d’Honneur at the Avignon Festival, which features a very large 40m-wide stage,” said Zanni. “The LSO function in version 2.1 offers an ‘intelligibility enhancement’ for spectators sitting in the very first rows, especially those who are placed on the opposite side of the on-stage performers. Based on the WFS pure rules, if a comedian, for example, performs on the very left front of the stage, the spectator placed 40m away, on the right of the audience, will hear a very low reinforcement level because of the WFS’ natural gain attenuation.”
Features for the Holophonix 2.1 update include macOS Ventura compatibility for Holophonix Native; Apple Silicon (ARM architecture) optimisation for Holophonix Native; new interfaces for source and bus creation; improvement of the presets loading; graphical enhancements on File and Display menus; and bug corrections. New additions include the Minimal Delay bus function for WFS; LSO function for WFS; a function enabling automatic bus creation from predefined speaker groups; and a function offering an automatic suggestion of the HOA order based on the number of speakers.